Criteria of proper engine radiator and intercooler selection – Thermotec
An efficient and well-functioning cooling system is one of the most important elements working on an engine. Its task is to keep the correct operating temperature of the engine. A higher temperature contributes to lower emissions of toxic compounds in the exhaust gases and also to lower combustion, but an uncontrolled rise to values significantly exceeding 100°C can cause excessive expansion of heated engine components and the possibility of breaking or cracking.The most important component of the cooling system is the radiator. A good quality radiator should feature:
- high thermal efficiency,
- high pressure resistance,
- corrosion resistance,
- long service life,
- in the case of non-original radiators, design as close to the original as possible.

Radiator production technology does matter!
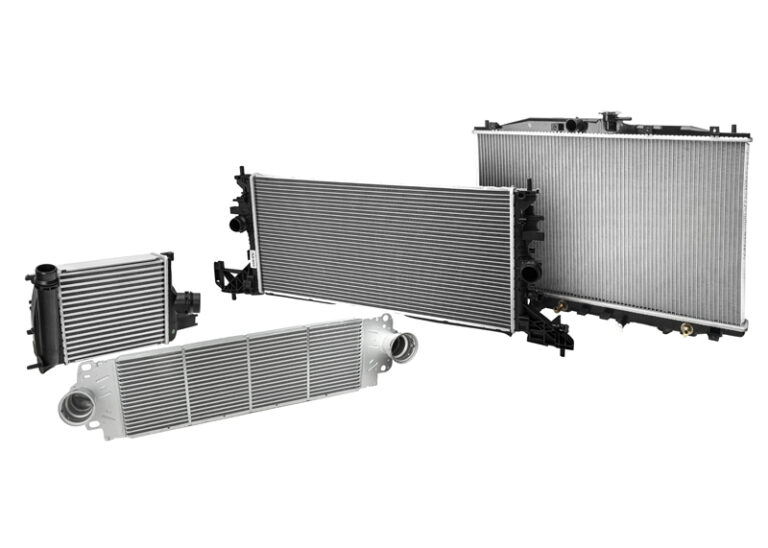
A very important issue affecting the final price of a radiator, which many buyers are not aware of, is the construction technology. There are two typical forms of connecting the radiator core to the tank – brazed and mechanically bonded radiators. The advantage of the former is greater strength and rigidity and a larger heat transfer surface area, the disadvantage is higher production costs. Mechanically bonded radiators are cheaper to produce, but are less rigid than brazed ones, with the risk of leakage due to engine vibration. In this case, it is very important to pay attention to the quality of the gaskets used by the manufacturers. The most popular and most common today are mechanically bonded radiators with round or oval tubes and brazed radiators, less so, made entirely of aluminum.
What to pay attention to when choosing a radiator?
In addition to the manufacturing technology, when selecting a new radiator, several important things should be taken into account:
- the dimensions of the core correspond to the dimensions of the original one, when dimensioning, it is important to remember that: the “height” dimension ALWAYS refers to the distance between the tanks, regardless of whether the radiator is horizontal or vertical,
- the thickness of the core must not be less than that of the original one,
- the number and diameter of the tubes must be at least the same as in the original one,
- the fin density must not be less than that of the original one,
- the type of radiator, the construction of the core, and the material from which it is made should correspond to the original.
By keeping the above in mind, we considerably minimize the risk of purchasing a product that does not meet the requirements.
A defective radiator may result in insufficient cooling capacity, increased engine temperature, or a constantly running fan. The most common causes of these symptoms are usually a loss of coolant due to damage to the radiator, corroded or leaking connections, contaminated or possibly too old coolant, as well as the installation of a wrong radiator.
Intercooler- its significance
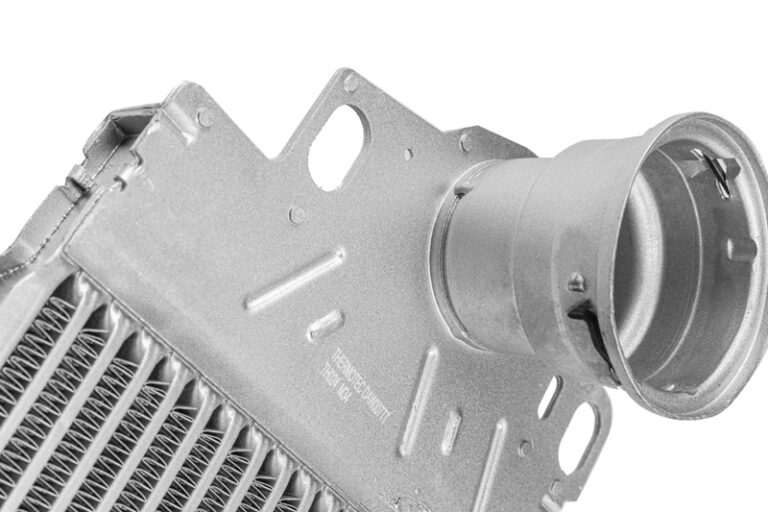
Increased power output, reduced fuel consumption, increased engine efficiency, improved exhaust gas quality, reduced thermal loads – there are many reasons for cooling the charge air. The air cooler (intercooler) is responsible for this. The design is similar to that of a radiator, but it is made using a different technology that allows operation at very high temperatures and pressures. The dimensions of the intercooler should be matched to the engine parameters and the turbocharger. An intercooler that is too large can lead to an increase in so-called turbocharging, i.e. a delayed response of the engine to pressing the accelerator. On the other hand, an intercooler that is too small will be a bottleneck in the intake system and will not allow the maximum capacity of the entire system to be developed.


